2/19/2020
Every time Tedros talks about how China is handling the situation he seems like he accepting an Academy Awards or something. Always thanking how China is doing a great job blah blah blah…

Plummeting iPhone production and a lack of new cars rolling off the assembly line dominated early discussion of coronavirus-induced shortages. But the epidemic currently sweeping China and making determined inroads into over two dozen other countries has forced hundreds of factories to close, affecting dozens of industries. If nothing else, coronavirus has made the world realize that globalization has its downsides.
It’s not just the virus itself that’s causing shortages, of course – rumors about the virus can be equally as devastating. Hong Kong, which is heavily dependent on China for many staples, has seen store aisles stripped of necessities like toilet paper, rice, and pasta in recent weeks as panic-buying ramps up while some factories struggle to reopen. Mere rumors of a toilet paper shortage earlier this month were enough to send thousands of locals pouring into stores to denude the shelves, triggering a rebuke from the government to those people “with evil intentions” spreading falsehoods “leading to panic buying and even chaos.”
At the same time the virus disrupts its exports, China is having a difficult time getting meat into the country, its own pork supply decimated by a recent outbreak of African swine fever. The US, Europe, and Brazil are still shipping meat to China, but the refrigerated containers have to be handled carefully, plugged in as soon as they’re unloaded to keep the meat cold and moved out quickly to make way for other containers.

Citywide quarantines have limited the supply of workers to move meat in Shanghai and Xingang, meaning much never makes it off the ship.
If anyone was hoping to break the monotony of quarantine with a little gym time, they’re out of luck unless they already have the duds. Athletic-wear behemoth UnderArmour revealed that coronavirus-related delays were causing shortages of fabric, packaging and raw materials, potentially reducing first-quarter revenues by up to $60 million.
They’re far from the only clothing brand hit hard by the outbreak – London-based designer Xuzhi Chen lamented that his clothes are manufactured in Shanghai, and he doesn’t know when production will be back online. He’s not alone in his plight – plenty of western brands have clothes made in China.

At the same time, Chinese buyers have stayed home from fashion shows in Milan and London, hitting even those Italian, and British brands that do their manufacturing at home hard.
Selling a niche product doesn’t guarantee safety from the ravages of virus-related factory closures, either. The owner of a chain of Russian sex shops revealed he was feeling the coronavirus squeeze in an interview with Gazeta, lamenting that many of the products he sells are either made in China or have major components sourced from China.
Condom shortages in Singapore and Hong Kong would at first seem to suggest that people are using their quarantine time to get hot and heavy, but photos circulating on social media indicate the prophylactics are flying off the shelves for other reasons – to cover for shortages of gloves and masks, to start. About a quarter of the world’s condoms are made in China.
Even sports stars have had to deal with coronavirus-induced shortages, a problem they might have expected their celebrity to insulate them from. Bauer Hockey, which makes custom hockey sticks for elite customers including many NHL players, saw its factory in Tongxiang City in Zhejiang province shut down last month and delay reopening twice.
The issue has apparently caused ripples in the league, leading to players being restricted to a “one-stick limit for practice and maybe two for games.” A player might typically go through several sticks in a single game, so while the shortage is very much a “first world problem,” it has caused much consternation in the hockey world.

Coronavirus’ economic impact is likely to be felt far into the future. A handful of major trade shows have either been put on hold or canceled altogether, most notably the Mobile World Congress, the world’s largest smartphone trade show. Scheduled for later this month in Barcelona, the conference – which typically hosts 100,000 attendees – has been completely called off. Smaller events for brands like Swatch and Cisco have also gotten the axe. Even gatherings still on the calendar, like this week’s Singapore Airshow, will see attendance severely curtailed as over 70 exhibitors have pulled out. Multi-million-dollar deals that might have been sealed at these temples of commerce will fall by the wayside or be postponed until the return of a favorable business climate – and no one knows quite when that will be.
The virus has disrupted next week’s Berlin Film Festival, with over 50 Chinese delegates and several other international execs pulling out because they couldn’t get travel visas. The festival is supposed to include three Chinese features and one short, which presumably will be screened anyway – even if their directors are stuck home in quarantine. But with China an ever larger international market for films, the absence of the executives will be felt.
And the virus has caused behaviors to change even where it hasn’t reached epidemic levels. People are thinking twice before having unnecessary contact with others, and redefining what contact might be “necessary.” Our Lady’s Acomb Church in York has pressed pause on its Communion ritual, which involves drinking wine out of a communal chalice, “until further notice” – lest an infected parishioner sicken others.
Such symbolic attempts to stave off an uncertain, invisible threat exemplify the global response to an epidemic that is still not well understood: a combination of panic and prayer.

by Shane Trejo
Mario Draghi, president of the European Central Bank (ECB) and Christine Lagarde, managing director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), are urging Trump to abandon his trade war and return to the status quo preferred by globalist financiers.
“We meet at a moment when support for global cooperation and multilateral solutions is waning,” Lagarde said at the 8th ECB conference for the central, eastern and south-eastern European (CESEE) nations on Wednesday.
“Global growth has been subdued for more than six years and the largest economies in the world are putting up, or threatening to put up, new trade barriers. And this might be the beginning of something else, which might affect us all in a more broad way,” she added.
Lagarde also warned: “These troubling developments will create headwinds for all, but certainly for the CESEE growth model, a model that has relied on openness and integration.”
Draghi also forecast doom unless Trump submitted to China, abandoned his nationalistic policies, and let he and his fellow bankster cronies go back to running the global economy.
“Global trade has faced headwinds in recent years as trade-restrictive measures have outpaced liberalising measures,” Draghi said.
“The central and eastern European business model has become vulnerable to shocks to international trade and financial conditions,” he added, warning of potential ill effects of Trump threatening to hike tariffs on European autos.
“The effect of tariffs could be amplified, as a large share of goods cross borders multiple times during the production process,” Draghi said.
“The main long-term challenge is moving towards a more balanced growth and financing model, which is more reliant on domestic innovation and on higher investment spending than it has been so far,” he added.
Regardless of the fear-mongering of the international bankers, President Trump remains undaunted in his resolve to cut China down to size and approve the standing of the U.S. in the world.
Mac Slavo
December 19th, 2018

By Mac Slavo
December 19th, 2018
According to NPR, the Fed last raised rates in September. Since then, the U.S. economy has given off mixed signals. The job market remains strong, with unemployment at the lowest level in nearly 50 years and economic growth clocked in at a solid 3.5 percent in the third quarter. But the stock market is stumbling and home sales and car sales have slumped because of the higher interest rates. Not to mention the ongoing trade tensions between the United States and China which have led to growing fears about the outlook for the global economy.
President Donald Trump has even taken to Twitter to announce the Fed’s plan to hike interest rates again.
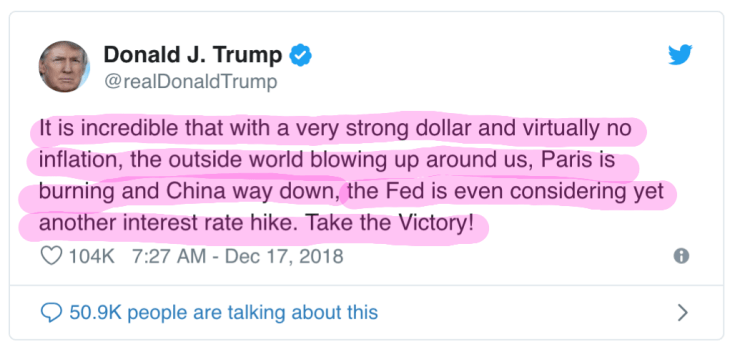
The decision to raise the interest rate will affect the rates on all kinds of borrowing, from home mortgages to credit cards. The 30-year mortgage rate in the past year climbed from 3.95 percent to a peak of nearly 5 percent in November, which is a seven-year high. It has since dropped to 4.63 percent, still higher than most borrowers would want.
Trump also called the Fed the “greatest threat” in October in an interview with Fox Business, and has singled out Fed chairman Jerome Powell for harsh criticisms., of which the central bank is in desperate need of. The Fed is answerable to no one and usually insulated from political pressure. Presidents in recent times, including Trump’s predecessors, Barack Obama, and George W. Bush, have refrained from overtly criticizing the central bank, probably because they collude with the government for economic destruction.

Meanwhile, Powell has said that the economic outlook remains solid and that interest rates are nearly within a “neutral” range which seems to be indicating that the Fed may not be immediately worried about any inflation. “Interest rates are still low by historical standards,” he said in November.
Stock prices have fallen sharply since early November and it is somewhat rare for the Fed to raise rates in the face of a sustained market selloff. So there’s an outside chance the Fed could change course and pull a stunner by keeping rates steady at the Wednesday meeting.